About Scabies
Scabies is an itchy skin infection caused by a tiny skin mite that bores itself into the upper layer of the human skin causing an infection.
CAUSES
RISK FACTORS
It is commonly seen in children and their mothers as well as teenagers who are sexually active. Those who live in nursing and other care homes are likely candidates for scabies. Nursing homes, extended care facilities, prisons, and even child care facilities are institutions that most commonly have scabies outbreaks. Anyone who has a weakened immune system is susceptible to easily contracting it.
Intense Itching can cause skin sores that can lead to infection by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or beta-hemolytic
streptococci.
SYMPTOMS
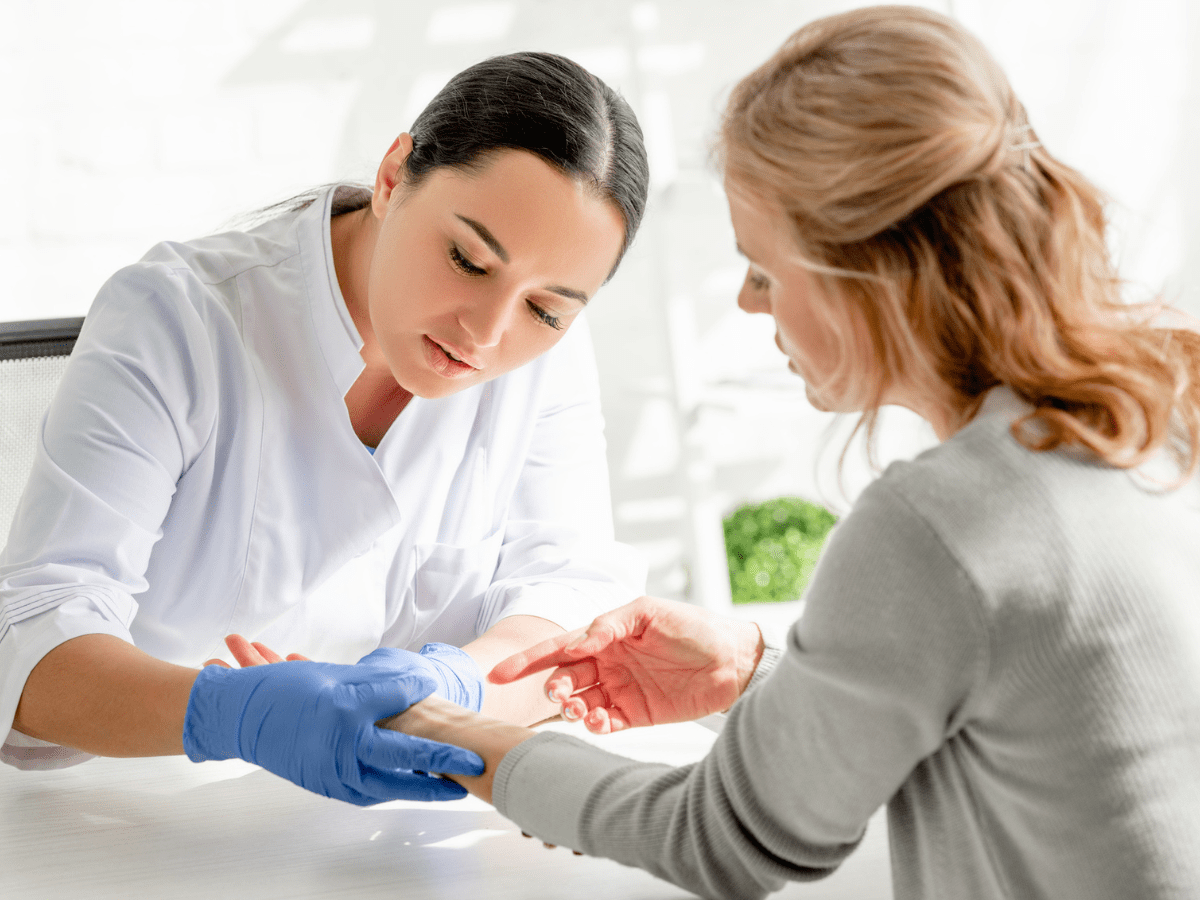
DIAGNOSIS
A doctor will perform a skin examination In order to diagnose scabies and will most likely remove a bit of the infected area and inspect it under a microscope.
Diagnosis is often made by the appearance of rash and presence of burrows. When possible it should be confirmed by finding mites, mite eggs, or fecal matter.
Visit Virginia Dermatology & Skin Cancer Center
Our team provides thoughtful, expert care for all your general, surgical and cosmetic dermatological needs. We are proud to offer the most advanced dermatological services in Norfolk, Suffolk, Newport News, and surrounding areas.