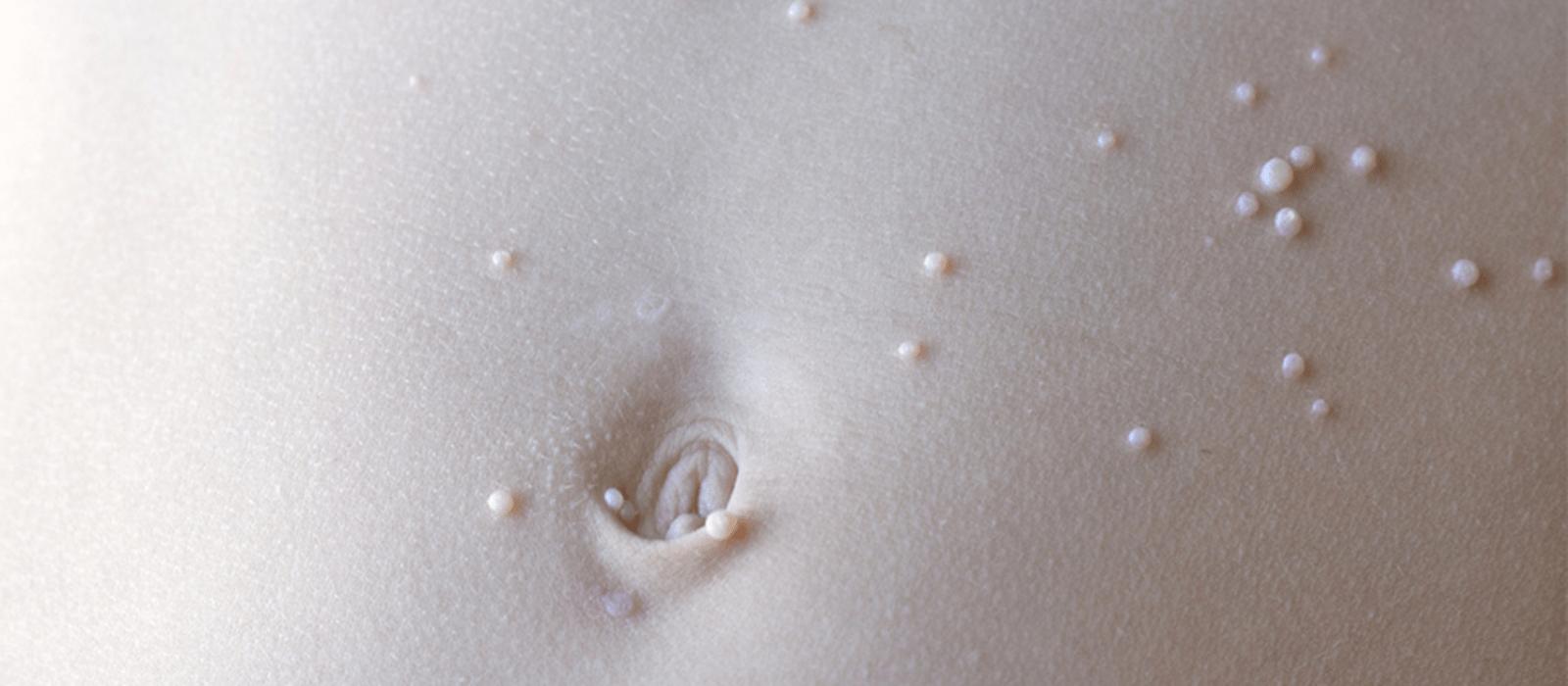
About Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum Contagiosum is a common skin disease. The disease is generally mild and should not be a reason for concern or worry.
CAUSES
Molluscum Contagiosum is a skin infection caused by a specific virus. This virus is contagious and can be spread by direct contact.
RISK FACTORS
This skin disease can cause the bumps to spread to different parts of the body. This is called autoinoculation. Such spread can occur by touching or scratching a bump and then touching another part of the body. The virus can also be spread from person to person. This can happen if the growths on one person are touched by another person. It can also happen if the virus gets on an object that is touched by other people, such as sharing towels, clothing, and toys. Molluscum can also be spread from one person to another by sexual contact. Anyone who develops bumps in the genital area (on or near the penis, vulva, vagina, or anus) should see a health care provider. Bumps in these areas sometimes mean that molluscum or some other disease was spread through sexual contact.
The below items may put you at a greater risk for contracting molluscum contagiosum:
• Tropical or warm, humid climates.
• Weakened immune system, particularly in those with HIV.
• Those with atopic dermatitis.
• Overcrowded conditions.
• Sexual contact.
• Poor hygiene.
SYMPTOMS
Molluscum infection causes small white, pink, or flesh-colored bumps or growths with a dimple or pit in the center. The bumps are usually smooth and firm and can appear anywhere on the body. They may become sore, red, and swollen but are usually painless. The bumps normally disappear within 6 to 12 months without treatment and without leaving scars. In people with weakened immune systems, molluscum growths may grow very large, spread more easily to other parts of the body and may be harder to cure.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis is usually made by the characteristic appearance of the lesion. It may also be diagnosed by collecting a specimen from the lesion, called a biopsy. Biopsies are routinely performed in dermatology offices.
PREVENTION
There are multiple ways to prevent the spread or contraction of molluscum contagiosum. Some of these include:
• Washing hands thoroughly and frequently if you or a family member are infected.
• Not scratching at or picking at lesions.
• Keeping lesions covered.
• Keeping skin moisturized, as breaks in the skin barrier from dry skin or eczema can hasten the spread of lesions.
• If you are infected, do not take part in contact sports, such as wrestling, basketball, or football.
• Avoid swimming unless you can cover lesions with watertight bandages. Keep lesions covered with bandages and if
swimming, use watertight bandages.
• Do not share personal items, such as towels, unwashed clothing, watches, bar soap, etc.
• Avoid sexual contact.
Visit Virginia Dermatology & Skin Cancer Center
Our team provides thoughtful, expert care for all your general, surgical and cosmetic dermatological needs. We are proud to offer the most advanced dermatological services in Norfolk, Suffolk, Newport News, and surrounding areas.