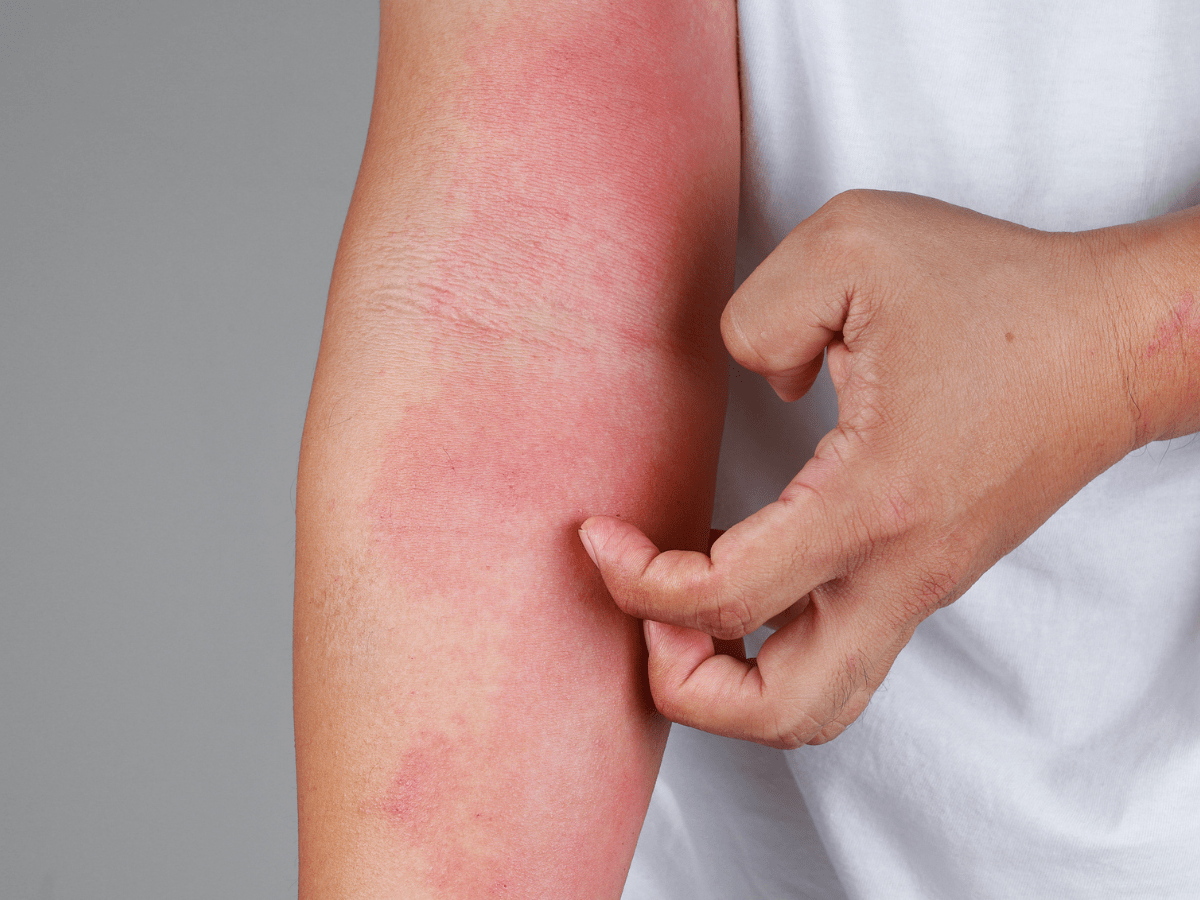
About Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is inflammation of the skin that results from direct contact of a substance with the surface of the skin, which may or may not be related to an allergy. Some substances are always irritating to the skin.
 Irritant Contact Dermatitis
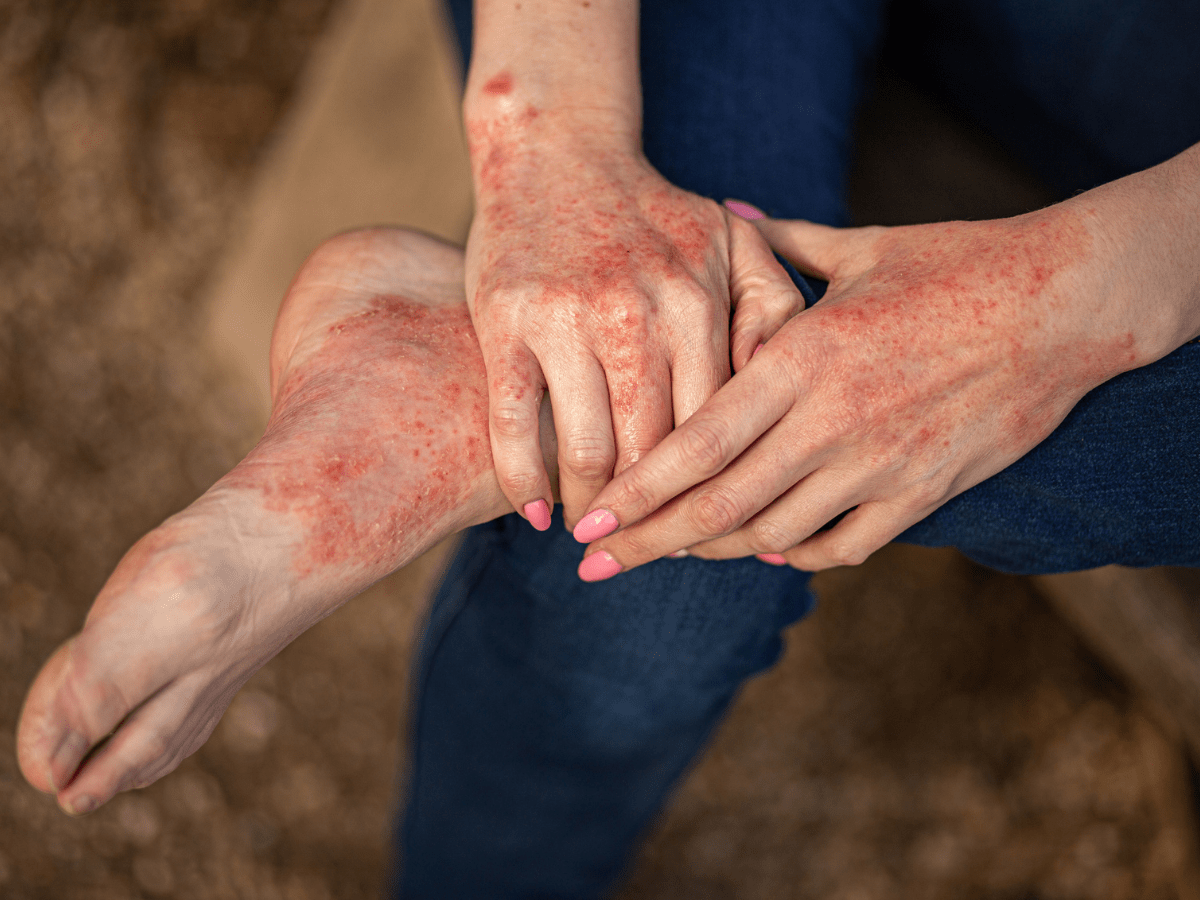
Irritant Contact DermatitisThe most common form and develops when substances such as solvents or other chemicals irritate the skin. The exposure produces red, often more painful than itchy, patches on the involved skin areas.
 Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic Contact DermatitisAn immune response triggered by an allergen, such as nickel, perfumes, dyes, rubber, latex, topical medications and cosmetics. More than 3,600 substances can cause allergic contact dermatitis.
CAUSES
A person develops contact dermatitis when something that touches the skin does one of the following:
- Irritates the skin
- Causes an allergic reaction
RISK FACTORS
Anyone can develop contact dermatitis. Your risk factor may be increased if you are in regular contact with an irritant or allergen, or if you already have allergies to certain substances, such as plants, chemicals, or medications. People working in certain professions have a higher risk. Sometimes this is referred to as occupational dermatitis. It is important to know that the more you come in contact with a substance, the more likely you are to develop an allergy to it and for it to be the cause of allergic contact dermatitis.
SYMPTOMS
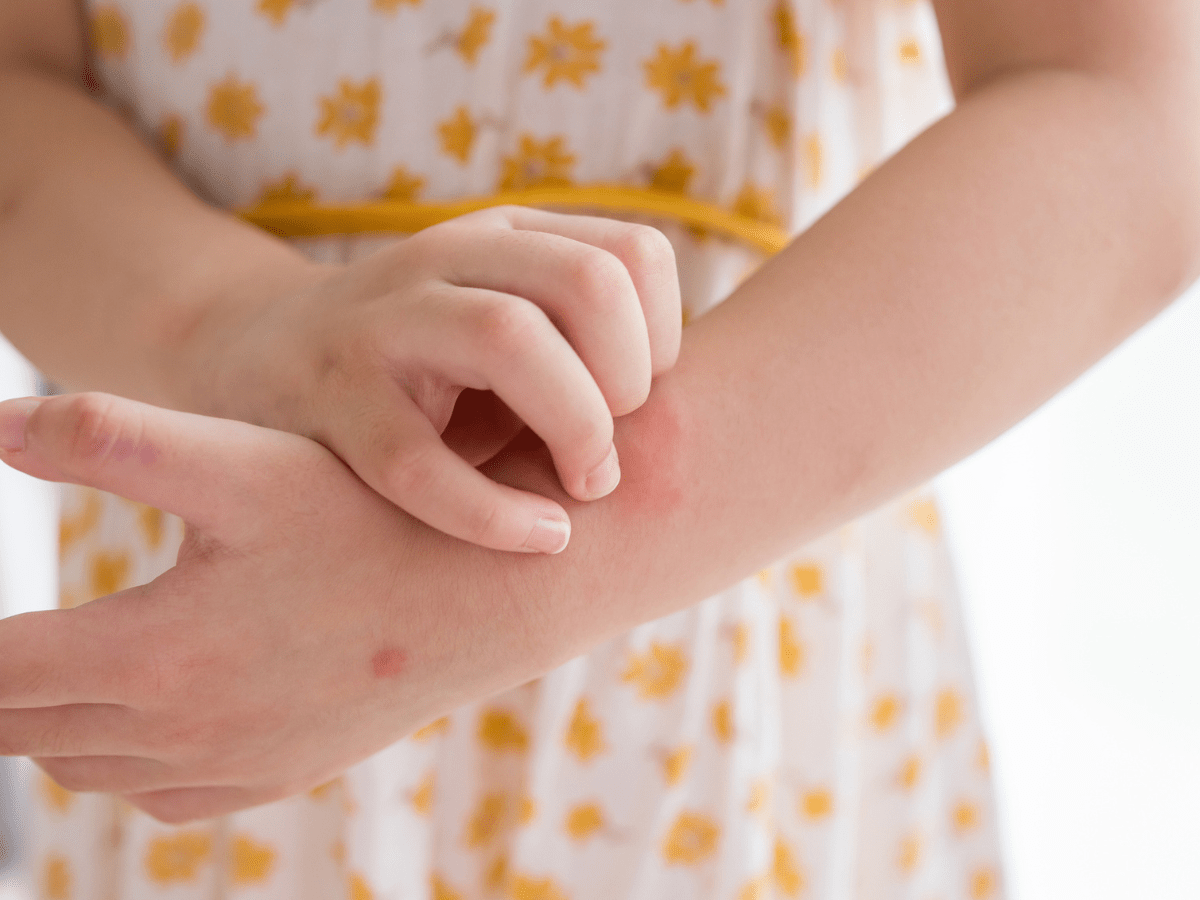
Signs and symptoms of contact dermatitis rarely appear with immediate contact. Most symptoms of contact dermatitis appear within 24-72 hours. An allergic reaction requires more than 1 exposure to the substance, but after this, a reaction can occur quickly. Rarely, people can develop a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis (an-uh-fuh-lax-sis). If anyone has any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical care.
REACTIONS
When signs and symptoms do appear, you may have:
- Itchy skin, which can be intense
- Rash, including red, swollen, hot skin
- Excessively dry skin
- Burning
- Stinging
- Hives, which are round welts on the skin that itch
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Oozing blisters that leave crusts and scales
If exposure to the allergen continues, your skin may:
- Flake and crack
- Become scaly
- Darken, thicken, and feel leathery
DIAGNOSIS
To diagnose this common skin condition, dermatologists:
- Examine your skin and the developing rash
- Review your medical history
- Ask questions about your lifestyle to determine what may be causing the rash
If your dermatologist suspects that you have an allergy, patch testing may be recommended. A patch test involves applying panels to your skin that contain small amounts of possible allergens for a period of time. After this time, the patches are removed to inspect the skin for reactions. Relevance must be kept in mind when considering the results of a patch test. For instance, if the substance a patient reacts to is not something they come in contact with regularly, it is not likely to be the source of the contact dermatitis.
Visit Virginia Dermatology & Skin Cancer Center
Our team provides thoughtful, expert care for all your general, surgical and cosmetic dermatological needs. We are proud to offer the most advanced dermatological services in Norfolk, Suffolk, Newport News, and surrounding areas.